Data migration to the cloud has become a pivotal strategy for organizations seeking to capitalize on the advantages of cloud computing. Moving data from on-premise servers to cloud-based platforms not only offers businesses enhanced scalability and cost savings, but it also improves data accessibility and security.
This guide aims to provide a detailed overview of cloud migration, covering its benefits, challenges, real-world case studies, emerging trends, and best practices. Whether you’re a business leader, IT professional, or just curious about the cloud, this comprehensive exploration will equip you with the knowledge necessary to navigate the cloud migration journey successfully.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Data Migration to the Cloud?
At its core, data migration to the cloud involves transferring data, applications, and other digital assets from an organization’s internal servers or databases to a cloud environment such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), or Microsoft Azure. Cloud migration can be partial (hybrid cloud) or complete, depending on the organization’s needs and strategy.
The driving force behind cloud migration is the growing need for businesses to remain agile, responsive to market changes, and capable of handling vast amounts of data efficiently.
Key Benefits of Data Migration to the Cloud
The decision to migrate data to the cloud is often fueled by the numerous benefits cloud computing provides. Let’s delve into some of the most impactful advantages:
1. Cost Optimization
One of the most significant reasons companies choose cloud migration is the potential for cost savings. Cloud platforms offer pay-as-you-go models, which means businesses only pay for the storage and computing power they use. This eliminates the need for expensive on-premise infrastructure and maintenance.
For example, Netflix, one of the world’s largest streaming platforms, reduced its infrastructure costs by 50% after migrating over 100 petabytes of data to AWS. By transitioning to the cloud, Netflix not only optimized costs but also gained the flexibility to scale resources dynamically to meet the ever-growing demands of its global audience.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
In an era where businesses need to remain competitive and agile, the cloud offers unparalleled scalability. Whether an organization needs to scale up during periods of high demand or scale down during quieter times, the cloud provides the flexibility to adapt quickly.
This scalability allows organizations to expand their operations without worrying about outgrowing their data infrastructure. Airbnb, for instance, migrated over 1 billion listings to Microsoft Azure, improving scalability and enabling global expansion while maintaining high data security and compliance standards.
3. Improved Data Accessibility
Migrating to the cloud significantly improves data accessibility. Employees and stakeholders can access data and applications from any location, at any time, provided they have an internet connection. This fosters collaboration, enhances productivity, and supports remote working environments—a crucial advantage in today’s post-pandemic world.
With cloud-based platforms, businesses can also ensure that their data is backed up and accessible in the event of a disaster, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity.
4. Enhanced Security
Cloud platforms invest heavily in robust security measures, including encryption, multi-factor authentication, and advanced threat detection. Migrating to the cloud enables businesses to leverage these advanced security features, reducing the risk of data breaches and cyberattacks.
Companies like Spotify, which migrated over 100 million music tracks to GCP, took advantage of cloud security to protect user data while enhancing the overall user experience.
Challenges of Data Migration to the Cloud
While the benefits of cloud migration are immense, businesses may encounter several challenges during the migration process. It’s crucial to understand these challenges to mitigate risks and ensure a smooth transition:
1. Data Security and Compliance
Data security is a significant concern when migrating sensitive information to the cloud. Businesses must ensure that their cloud provider complies with industry regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act). Encrypting data and implementing secure access controls are essential steps in protecting data during and after migration.
2. Downtime and Disruptions
Migrating large volumes of data can cause disruptions in service, leading to downtime. Planning the migration process meticulously, scheduling it during off-peak hours, and conducting tests to identify potential issues are essential to minimizing disruptions.
3. Data Loss and Integrity
There is always the risk of data loss during migration, especially when transferring vast amounts of information. Ensuring data integrity through regular backups and using tools that verify data accuracy after the migration is critical.
4. Skilled Expertise
Migrating to the cloud requires specialized skills in cloud architecture, data management, and cybersecurity. Organizations may need to invest in training or hire experts to manage the complexities of the migration process.
Case Studies: Successful Data Migrations to the Cloud
Real-world case studies can provide valuable insights into the potential impact of data migration to the cloud. Here are a few examples of organizations that successfully leveraged the cloud to transform their operations:
Netflix: Reducing Costs and Enhancing Scalability
As one of the earliest adopters of cloud technology, Netflix successfully migrated its vast content library, consisting of over 100 petabytes of data, to AWS. The transition helped Netflix reduce infrastructure costs by 50% and scale seamlessly to meet the growing demand from its global user base. The flexibility and performance enhancements gained from the migration enabled Netflix to focus on delivering a superior user experience, without the burden of managing on-premise servers.
Spotify: Improving User Experience Through Cloud Migration
Spotify moved over 100 million music tracks to Google Cloud Platform (GCP), improving latency and providing real-time analytics for personalized recommendations. By leveraging the cloud, Spotify enhanced its ability to deliver smooth music streaming experiences, while using AI and machine learning for real-time data insights, thus improving user engagement and satisfaction.
Airbnb: Enabling Global Expansion and Compliance
Airbnb migrated over 1 billion property listings to Microsoft Azure, improving both data security and scalability. The migration enabled Airbnb to expand globally, offering more flexible accommodation options to users around the world, while maintaining compliance with data protection regulations in various jurisdictions.
These case studies highlight the potential for cloud migration to transform businesses by reducing costs, improving scalability, and enhancing overall performance.
Emerging Trends in Data Migration to the Cloud
As the cloud landscape continues to evolve, new trends are shaping the future of data migration. Two of the most significant trends involve the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to automate and optimize the migration process.
AI and ML in Data Migration
AI and ML are increasingly being used to streamline cloud migration efforts. By automating key aspects of the migration process, AI and ML can:
- Classify and prioritize data: AI helps identify which data should be migrated first, minimizing downtime and disruptions.
- Create optimized migration plans: AI algorithms analyze system workloads to determine the most efficient migration path.
- Predict migration time and resources: ML models can predict how long the migration process will take and what resources will be required.
- Monitor and resolve issues: AI-powered tools continuously monitor the migration process, identifying and resolving errors in real time.
Although the use of AI and ML in cloud migration is still in its early stages, these technologies have the potential to revolutionize the way organizations move data to the cloud, making the process faster, more efficient, and less prone to human error.
Best Practices for Data Migration to the Cloud
To ensure a successful migration, organizations should follow best practices that minimize risks and maximize benefits:
1. Plan and Prepare
Proper planning is the cornerstone of a successful cloud migration. Organizations should:
- Define their migration goals and objectives.
- Assess current infrastructure and identify which data and applications need to be migrated.
- Develop a migration timeline to minimize downtime.
2. Choose the Right Tools
Selecting the appropriate migration tools is crucial for a smooth transition. There are various cloud-native tools provided by platforms like AWS, GCP, and Azure, designed to simplify the migration process.
3. Ensure Data Security
Implementing robust security measures is essential when migrating sensitive data. Encryption, multi-factor authentication, and access controls should be employed to protect data during the migration process.
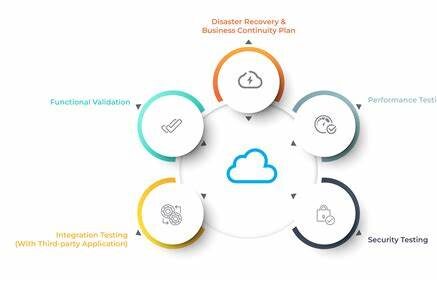
4. Test Thoroughly
Before completing the migration, organizations should conduct thorough testing to ensure that data has been transferred accurately and that systems are performing as expected. Testing also helps to identify and resolve any potential issues before going live.
Conclusion: Unlocking the Full Potential of Cloud Migration
Migrating data to the cloud offers businesses a wide range of advantages, including cost savings, improved scalability, enhanced data accessibility, and robust security. By following best practices, addressing potential challenges, and staying updated on emerging trends like AI and ML, organizations can successfully harness the power of cloud computing to stay ahead in an increasingly competitive digital landscape.
For more detailed insights on cloud computing and migration strategies, visit Cloud Migration Strategies.