Step-by-step guide to investing in stocks introduces you to the world of stock investment, providing valuable insights and practical tips to help you navigate this complex market with confidence.
Whether you’re a beginner looking to start your investment journey or an experienced investor seeking to enhance your portfolio, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools needed to make informed decisions and achieve your financial goals.
Introduction to Stock Investment
Investing in stocks is a way for individuals to own a part of a company and participate in its growth and success. When you buy a stock, you are essentially buying a small piece of ownership in that company.
What are Stocks and How Do They Work?
Stocks represent shares of ownership in a company. When you buy a stock, you become a shareholder and have a claim on the company’s assets and earnings. The value of a stock can fluctuate based on the company’s performance, market conditions, and other factors. Investors can make money through capital appreciation (when the stock price increases) and dividends (payments made by the company to its shareholders).
Potential Benefits of Investing in Stocks
- Opportunity for Growth: Stocks have the potential to generate significant returns over the long term, outpacing inflation and other investment options.
- Diversification: Investing in a variety of stocks can help spread risk and reduce the impact of market volatility on your portfolio.
- Dividend Income: Some companies pay dividends to their shareholders, providing a source of passive income.
- Liquidity: Stocks are generally easy to buy and sell, making them a liquid investment that can be quickly converted into cash.
- Ownership Rights: Shareholders have the right to vote on company decisions and attend shareholder meetings, giving them a say in how the company is run.
Getting Started with Stock Investing

Investing in stocks can be a great way to grow your wealth over time, but it’s essential to approach it with the right strategy. Here are some basic steps to help you get started with stock investing:
Key Factors to Consider Before Investing
- Assess your financial situation: Before diving into stock investing, it’s crucial to evaluate your current financial position, including your income, expenses, debts, and savings.
- Educate yourself: Take the time to learn about the stock market, different investment options, and the risks involved. Knowledge is key to making informed investment decisions.
- Define your risk tolerance: Understand how much risk you are willing to take with your investments. Your risk tolerance will determine the type of stocks you should consider.
- Consider your investment goals: Whether you’re investing for retirement, a major purchase, or wealth accumulation, setting clear investment goals will help you stay focused and make better investment choices.
Importance of Setting Investment Goals
Setting investment goals is a crucial step in stock investing because it helps you:
- Stay motivated and disciplined: Having clear goals will keep you focused on your long-term financial objectives, helping you avoid impulsive decisions.
- Measure your progress: By setting specific targets, you can track how well your investments are performing and make adjustments as needed.
- Align your investments with your aspirations: Whether you aim to build a retirement fund, save for a home, or achieve financial independence, setting goals ensures your investments are in line with your objectives.
Types of Stocks to Invest In

When investing in stocks, it’s important to understand the different types available to make informed decisions. Common stock and preferred stock are the two main categories of stocks that investors can choose from. Let’s explore the characteristics, differences, and risks associated with each type of stock.
Common Stock, Step-by-step guide to investing in stocks
Common stock represents ownership in a company and gives shareholders voting rights at annual meetings. Investors in common stock have the potential for high returns through capital appreciation and dividends. However, they are also exposed to more risk compared to preferred stockholders. In the event of bankruptcy, common stockholders are the last to receive any remaining assets after creditors and preferred stockholders.
Preferred Stock
Preferred stock is a type of stock that gives shareholders priority over common stockholders in terms of dividends and asset distribution in the event of liquidation. Preferred stockholders do not usually have voting rights, but they receive fixed dividends that must be paid before dividends can be distributed to common stockholders. While preferred stock offers more stability and consistent income compared to common stock, it may not provide as much potential for capital appreciation.
When it comes to risks, common stock tends to be more volatile and subject to market fluctuations compared to preferred stock. Preferred stock, on the other hand, may be more sensitive to interest rate changes and is generally less liquid than common stock.
Overall, the choice between common stock and preferred stock depends on an investor’s risk tolerance, income objectives, and investment goals. It’s essential to carefully assess the characteristics and risks associated with each type of stock before making investment decisions.
How to Analyze Stocks
When it comes to investing in stocks, analyzing the performance and potential of a stock is crucial to making informed decisions. There are two main approaches to analyzing stocks: fundamental analysis and technical analysis. Fundamental analysis focuses on evaluating a company’s financial health, management team, competitive position, and industry trends. On the other hand, technical analysis involves studying historical price and volume data to predict future price movements.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis involves looking at various factors to determine the intrinsic value of a stock. Key metrics used in fundamental analysis include:
- Earnings Per Share (EPS): This measures a company’s profitability by dividing its total earnings by the number of outstanding shares.
- Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio: This ratio compares a company’s stock price to its earnings per share, indicating whether a stock is overvalued or undervalued.
- Debt-to-Equity ratio: This ratio shows how much debt a company has compared to its equity, providing insight into its financial leverage.
- Return on Equity (ROE): ROE measures a company’s profitability by showing how much profit it generates with the shareholders’ equity.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis involves using charts and statistical indicators to forecast future price movements. Key metrics used in technical analysis include:
- Moving Averages: These are used to smooth out price data and identify trends over a specific period.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): RSI is a momentum oscillator that measures the speed and change of price movements.
- Bollinger Bands: These bands indicate volatility and potential price breakouts based on standard deviations from a moving average.
- Volume: Volume measures the number of shares traded, providing insight into the strength of a price movement.
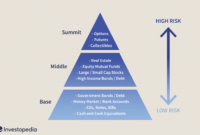
Building a Diversified Portfolio
Building a diversified portfolio is essential in stock investing to spread out risk and maximize returns. By investing in a variety of stocks across different sectors and industries, you can reduce the impact of volatility on your overall portfolio.
Strategies for Building a Diversified Portfolio
- Invest in stocks from different industries: By diversifying across sectors such as technology, healthcare, finance, and consumer goods, you can reduce sector-specific risks.
- Include different market capitalizations: Investing in large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap stocks can provide exposure to companies of varying sizes and growth potential.
- Consider international stocks: Adding international stocks to your portfolio can help spread geographical risk and provide exposure to global economic trends.
- Utilize exchange-traded funds (ETFs): ETFs offer a simple way to gain exposure to a diversified set of stocks or assets in a single investment.
The Importance of Asset Allocation in Portfolio Management
Asset allocation involves dividing your investment portfolio among different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and cash equivalents, based on your risk tolerance and investment goals. A well-balanced asset allocation can help manage risk and optimize returns over the long term.
Examples of How Diversification Can Mitigate Risk
- Diversification reduces company-specific risk: By holding a mix of stocks from different companies, you can minimize the impact of negative events that may affect individual companies.
- Geographical diversification lowers country-specific risk: Investing in stocks from various countries can protect your portfolio from local economic downturns or geopolitical events.
- Sector diversification mitigates industry-specific risk: Allocating investments across different sectors can shield your portfolio from sector-wide volatility or regulatory changes.
Risks and Challenges in Stock Investing

Investing in stocks can offer great potential for growth and wealth accumulation, but it also comes with its fair share of risks and challenges. Understanding these risks and knowing how to manage them is crucial for any investor looking to navigate the stock market successfully.
Market Volatility
Market volatility is a common risk associated with stock investing. Prices of stocks can fluctuate rapidly in response to various factors such as economic indicators, geopolitical events, or company news. To manage this risk, investors should focus on long-term goals, diversify their portfolio, and avoid making impulsive decisions based on short-term market movements.
Company-specific Risks
Investing in individual stocks exposes investors to company-specific risks such as poor management decisions, regulatory issues, or product failures. To mitigate this risk, investors should conduct thorough research on the companies they are investing in, analyze their financial health and growth prospects, and stay informed about any developments that could impact the company’s performance.
Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk refers to the possibility of not being able to buy or sell a stock quickly at a fair price. This can happen when trading volumes are low or when there is a lack of market interest in a particular stock. To manage liquidity risk, investors should focus on investing in liquid stocks with high trading volumes and avoid investing in illiquid or thinly traded stocks.
Interest Rate Risk
Changes in interest rates can impact stock prices, especially for interest rate-sensitive sectors such as utilities or real estate. Investors should be aware of interest rate trends and how they can affect their stock investments. Diversifying across different sectors and asset classes can help mitigate the impact of interest rate risk on a portfolio.
Political and Economic Risks
Political and economic events can have a significant impact on the stock market. Factors such as changes in government policies, trade tensions, or economic recessions can lead to market volatility and affect stock prices. Investors should stay informed about macroeconomic trends, geopolitical developments, and policy changes that could impact their investments.
Monitoring and Rebalancing Your Stock Portfolio: Step-by-step Guide To Investing In Stocks
Monitoring and rebalancing your stock portfolio is crucial to ensure that your investments are aligned with your financial goals and risk tolerance. By actively monitoring your portfolio, you can make informed decisions based on market changes and performance.
Importance of Monitoring Your Stock Portfolio
- Regularly tracking the performance of your stocks allows you to identify any underperforming or overperforming assets.
- Monitoring helps you stay informed about market trends and news that could impact your investments.
- By assessing your portfolio regularly, you can make adjustments to maintain a balanced and diversified investment strategy.
When and How to Rebalance Your Portfolio
- Rebalancing your portfolio should be done periodically, such as annually or semi-annually, or when there are significant market shifts.
- To rebalance, review your asset allocation and adjust the weights of different stocks or asset classes to stay in line with your investment objectives.
- Consider selling off overperforming assets and reallocating funds to underperforming ones to maintain a balanced portfolio.
Tools and Resources for Tracking Portfolio Performance
- Utilize online brokerage platforms that offer portfolio tracking features, allowing you to monitor your investments in real-time.
- Financial news websites and apps provide up-to-date market information and analysis to help you make informed decisions about your portfolio.
- Consider using portfolio management software or apps that offer detailed insights into your asset allocation, performance, and risk metrics.
In conclusion, the Step-by-step guide to investing in stocks is your roadmap to building a successful investment portfolio and mastering the art of stock investing. By following the strategies Artikeld in this guide, you can navigate the ups and downs of the stock market with ease and achieve long-term financial growth.
When looking for the best investment options, keeping an eye on the top performing mutual funds is crucial. In 2024, investors are closely watching the market to see which funds are outperforming the rest. To stay updated on the latest trends and opportunities, make sure to check out the list of Top performing mutual funds 2024 for valuable insights.
When looking for the top performing mutual funds in 2024, it’s essential to consider various factors such as historical performance, fees, and fund manager expertise. You can find a detailed list of the top performing mutual funds 2024 to make informed investment decisions.